Sources of Financing
Finance is the lifeblood of business concern, because it is interlinked with all activities performed by the business concern.
In a human body, if blood circulation is not proper, body function will stop. Similarly, if the finance not being properly arranged, the business system will stop. Arrangement of the required finance to each department of business concern is highly a complex one and it needs careful decision.
Quantum of finance may be depending upon the nature and situation of the business concern. But, the requirement of the finance may be broadly classified into two parts:
Long-term Financial Requirements or Fixed Capital Requirement
Financial requirement of the business differs from firm to firm and the nature of the requirements on the basis of terms or period of financial requirement, it may be long term and short-term financial requirements.
Long-term financial requirement means the finance needed to acquire land and building for business concern, purchase of plant and machinery and other fixed expenditure.
Long-term financial requirement is also called as fixed capital requirements. Fixed capital is the capital, which is used to purchase the fixed assets of the firms such as land and building, furniture and fittings, plant and machinery, etc. Hence, it is also called a capital expenditure.
Short-term Financial Requirements or Working Capital Requirement apart from the capital expenditure of the firms, the firms should need certain expenditure like procurement of raw materials, payment of wages, day-to-day expenditures, etc. This kind of expenditure is to meet with the help of short-term financial requirements which will meet the operational expenditure of the firms. Short-term financial requirements are popularly known as working capital.
SOURCES OF FINANCING
Sources of finance mean the ways for mobilizing various terms of finance to the industrial concern. Sources of finance state that, how the companies are mobilizing finance for their requirements. The companies belong to the existing or the new which need sum amount of finance to meet the long-term and short-term requirements such as purchasing of fixed assets, construction of office building, purchase of raw materials and day-to-day expenses.
Sources of finance may be classified under various categories according to the following important heads:
1. Based on the Period
Sources of Finance may be classified under various categories based on the period. Long-term sources: Finance may be mobilized by long-term or short-term. When the finance mobilized with large amount and the repayable over the period will be more than five years, it may be considered as long-term sources. Share capital, issue of debenture, long-term loans from financial institutions and commercial banks come under this kind of source of finance. Long-term source of finance needs to meet the capital expenditure of the firms such as purchase of fixed assets, land and buildings, etc.
Sources of Finance may be classified under various categories based on the period. Long-term sources: Finance may be mobilized by long-term or short-term. When the finance mobilized with large amount and the repayable over the period will be more than five years, it may be considered as long-term sources. Share capital, issue of debenture, long-term loans from financial institutions and commercial banks come under this kind of source of finance. Long-term source of finance needs to meet the capital expenditure of the firms such as purchase of fixed assets, land and buildings, etc.
Long-term sources of finance include:
● Equity Shares
● Preference Shares
● Debenture
● Long-term Loans
● Fixed Deposits
Short-term sources: Apart from the long-term source of finance, firms can generate finance with the help of short-term sources like loans and advances from commercial banks, moneylenders, etc. Short-term source of finance needs to meet
the operational expenditure of the business concern.
the operational expenditure of the business concern.
Short-term source of finance include:
● Bank Credit
● Customer Advances
● Trade Credit
● Factoring
● Public Deposits
● Money Market Instruments
2. Based on Ownership
Sources of Finance may be classified under various categories based on the period:
Sources of Finance may be classified under various categories based on the period:
An ownership source of finance include
● Shares capital, earnings
● Retained earnings
● Surplus and Profits
● Shares capital, earnings
● Retained earnings
● Surplus and Profits
Borrowed capital include
● Debenture
● Bonds
● Public deposits
● Loans from Bank and Financial Institutions.
3. Based on Sources of Generation
Sources of Finance may be classified into various categories based on the period.
Sources of Finance may be classified into various categories based on the period.
Internal source of finance includes
● Retained earnings
● Depreciation funds
● Surplus
External sources of finance may be include
● Share capital
● Debenture
● Public deposits
● Loans from Banks and Financial institutions
4. Based in Mode of Finance
Security finance may be include
● Shares capital
● Debenture
Security finance may be include
● Shares capital
● Debenture
Retained earnings may include
● Retained earnings
● Depreciation funds
Loan finance may include
● Long-term loans from Financial Institutions
● Short-term loans from Commercial banks.
The above classifications are based on the nature and how the finance is mobilized from various sources. But the above sources of finance can be divided into three major classifications:
● Security Finance
● Internal Finance
● Loans Finance
● Security Finance
● Internal Finance
● Loans Finance
SECURITY FINANCE
If the finance is mobilized through issue of securities such as shares and debenture, it is
called as security finance. It is also called as corporate securities. This type of finance plays a major role in the field of deciding the capital structure of the company.
called as security finance. It is also called as corporate securities. This type of finance plays a major role in the field of deciding the capital structure of the company.
Characters of Security Finance
Security finance consists of the following important characters:
1. Long-term sources of finance.
2. It is also called as corporate securities.
3. Security finance includes both shares and debentures.
4. It plays a major role in deciding the capital structure of the company.
5. Repayment of finance is very limited.
6. It is a major part of the company’s total capitalization.
2. It is also called as corporate securities.
3. Security finance includes both shares and debentures.
4. It plays a major role in deciding the capital structure of the company.
5. Repayment of finance is very limited.
6. It is a major part of the company’s total capitalization.
Types of Security Finance
Security finance may be divided into two major types:
1. Ownership securities or capital stock.
2. Creditor-ship securities or debt capital.
1. Ownership securities or capital stock.
2. Creditor-ship securities or debt capital.
Ownership Securities
The ownership securities also called as capital stock, is commonly called as shares. Shares are the most Universal method of raising finance for the business concern. Ownership capital consists of the following types of securities.
● Equity Shares
● Preference Shares
● No par stock
● Deferred Shares
● Preference Shares
● No par stock
● Deferred Shares
EQUITY SHARES
Equity Shares also known as ordinary shares, which means, other than preference shares. Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company. They have a control over the management of the company. Equity shareholders are eligible to get dividend if the company earns profit. Equity share capital cannot be redeemed during the lifetime of the company. The liability of the equity shareholders is the value of unpaid value of shares.
Features of Equity Shares
Equity shares consist of the following important features:
1. Maturity of the shares: Equity shares have permanent nature of capital, which has no maturity period. It cannot be redeemed during the lifetime of the company.
2. Residual claim on income: Equity shareholders have the right to get income left after paying fixed rate of dividend to preference shareholder. The earnings or the income available to the shareholders is equal to the profit after tax minus preference dividend.
3. Residual claims on assets: If the company wound up, the ordinary or equity shareholders have the right to get the claims on assets. These rights are only available to the equity shareholders.
4. Right to control: Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company. Hence, they have power to control the management of the company and they have power to take any decision regarding the business operation.
5. Voting rights: Equity shareholders have voting rights in the meeting of the company with the help of voting right power; they can change or remove any decision of the business concern. Equity shareholders only have voting rights in the company meeting and also they can nominate proxy to participate and vote in the meeting instead of the shareholder.
6. Preemptive right: Equity shareholder preemptive rights. The preemptive right is the legal right of the existing shareholders. It is attested by the company in the first opportunity to purchase additional equity shares in proportion to their current holding capacity.
7. Limited liability: Equity shareholders are having only limited liability to the value of shares they have purchased. If the shareholders are having fully paid up shares, they have no liability.
For example: If the shareholder purchased 100
shares with the face value of $10 each. He paid only $900. His liability is only $100.
shares with the face value of $10 each. He paid only $900. His liability is only $100.
Total number of shares 100
Face value of shares $10
Liability of the shareholders is only unpaid value of the share (that is $100).
Advantages of Equity Shares
Equity shares are the most common and universally used shares to mobilize finance for
the company. It consists of the following advantages.
the company. It consists of the following advantages.
1. Permanent sources of finance: Equity share capital is belonging to long-term permanent nature of sources of finance, hence, it can be used for long-term or fixed capital requirement of the business concern.
2. Voting rights: Equity shareholders are the real owners of the company who have voting rights. This type of advantage is available only to the equity shareholders.
3. No fixed dividend: Equity shares do not create any obligation to pay a fixed rate of dividend. If the company earns profit, equity shareholders are eligible for profit, they are eligible to get dividend otherwise, and they cannot claim any dividend from the company.
4. Less cost of capital: Cost of capital is the major factor, which affects the value of the company. If the company wants to increase the value of the company, they have to use more share capital because, it consists of less cost of capital (Ke) while compared to other sources of finance.
5. Retained earnings: When the company have more share capital, it will be suitable for retained earnings which is the less cost sources of finance while compared to other sources of finance.
Disadvantages of Equity Shares
1. Irredeemable: Equity shares cannot be redeemed during the lifetime of the business concern. It is the most dangerous thing of over capitalization.
2. Obstacles in management: Equity shareholder can put obstacles in management by manipulation and organizing themselves. Because, they have power to contrast any decision which are against the wealth of the shareholders.
3. Leads to speculation: Equity shares dealings in share market lead to secularism during prosperous periods.
4. Limited income to investor: The Investors who desire to invest in safe securities with a fixed income have no attraction for equity shares.
5. No trading on equity: When the company raises capital only with the help of equity, the company cannot take the advantage of trading on equity.
PREFERENCE SHARES
The parts of corporate securities are called as preference shares. It is the shares, which have preferential right to get dividend and get back the initial investment at the time of winding up of the company. Preference shareholders are eligible to get fixed rate of dividend and they do not have voting rights.
Preference shares may be classified into the following major types:
1. Cumulative preference shares: Cumulative preference shares have right to claim dividends for those years which have no profits. If the company is unable to earn profit in any one or more years, C.P. Shares are unable to get any dividend but
they have right to get the comparative dividend for the previous years if the company earned profit.
2. Non-cumulative preference shares: Non-cumulative preference shares have no right to enjoy the above benefits. They are eligible to get only dividend if the company earns profit during the years. Otherwise, they cannot claim any dividend.
3. Redeemable preference shares: When, the preference shares have a fixed maturity period it becomes redeemable preference shares. It can be redeemable during the lifetime of the company. The Company Act has provided certain restrictions on the return of the redeemable preference shares.
Irredeemable Preference Shares
Irredeemable preference shares can be redeemed only when the company goes for liquidator. There is no fixed maturity period for such kind of preference shares.
Participating Preference Shares
Participating preference shareholders have right to participate extra profits after distributing the equity shareholders.
Non-Participating Preference Shares
Non-participating preference shareholders are not having any right to participate extra profits after distributing to the equity shareholders. Fixed rate of dividend is payable to the type of shareholders.
Convertible Preference Shares
Convertible preference shareholders have right to convert their holding into equity shares after a specific period. The articles of association must authorize the right of conversion.
Non-convertible Preference Shares
There shares, cannot be converted into equity shares from preference shares.
Features of Preference Shares
The following are the important features of the preference shares:
1. Maturity period: Normally preference shares have no fixed maturity period except in the case of redeemable preference shares. Preference shares can be redeemable only at the time of the company liquidation.
2. Residual claims on income: Preferential sharesholders have a residual claim on income. Fixed rate of dividend is payable to the preference shareholders.
3. Residual claims on assets: The first preference is given to the preference shareholders at the time of liquidation. If any extra Assets are available that should be distributed to equity shareholder.
4. Control of Management: Preference shareholder does not have any voting rights. Hence, they cannot have control over the management of the company.
Advantages of Preference Shares
Preference shares have the following important advantages.
1. Fixed dividend: The dividend rate is fixed in the case of preference shares. It is called as fixed income security because it provides a constant rate of income to the investors.
2. Cumulative dividends: Preference shares have another advantage which is called cumulative dividends. If the company does not earn any profit in any previous years, it can be cumulative with future period dividend.
3. Redemption: Preference Shares can be redeemable after a specific period except in the case of irredeemable preference shares. There is a fixed maturity period for repayment of the initial investment.
4. Participation: Participative preference sharesholders can participate in the surplus profit after distribution to the equity shareholders.
5. Convertibility: Convertibility preference shares can be converted into equity shares when the articles of association provide such conversion.
Disadvantages of Preference Shares
1. Expensive sources of finance: Preference shares have high expensive source of finance while compared to equity shares.
2. No voting right: Generally preference sharesholders do not have any voting rights. Hence they cannot have the control over the management of the company.
3. Fixed dividend only: Preference shares can get only fixed rate of dividend. They may not enjoy more profits of the company.
4. Permanent burden: Cumulative preference shares become a permanent burden so far as the payment of dividend is concerned. Because the company must pay the dividend for the unprofitable periods also.
5. Taxation: In the taxation point of view, preference shares dividend is not a deductible expense while calculating tax. But, interest is a deductible expense. Hence, it has disadvantage on the tax deduction point of view.
DEFERRED SHARES
Deferred shares also called as founder shares because these shares were normally issued to founders. The shareholders have a preferential right to get dividend before the preference shares and equity shares. According to Companies Act 1956 no public limited company or which is a subsidiary of a public company can issue deferred shares.
These shares were issued to the founder at small denomination to control over the management by the virtue of their voting rights.
NO PAR SHARES
When the shares are having no face value, it is said to be no par shares. The company issues this kind of shares which is divided into a number of specific shares without any specific denomination. The value of shares can be measured by dividing the real net worth of the company with the total number of shares.
CREDITOR-SHIP SECURITIES
Creditor-ship Securities also known as debt finance which means the finance is mobilized from the creditors. Debenture and Bonds are the two major parts of the Creditor-ship Securities.
Debentures
A Debenture is a document issued by the company. It is a certificate issued by the company
under its seal acknowledging a debt.
under its seal acknowledging a debt.
According to the Companies Act 1956, “debenture includes debenture stock, bonds and any other securities of a company whether constituting a charge of the assets of the company or not.”
Types of Debentures
Debentures may be divided into the following major types:
1. Unsecured debentures: Unsecured debentures are not given any security on assets of the company. It is also called simple or naked debentures. This type of debentures are treaded as unsecured creditors at the time of winding up of the company.
2. Secured debentures: Secured debentures are given security on assets of the company. It is also called as mortgaged debentures because these debentures are given against any mortgage of the assets of the company.
3. Redeemable debentures: These debentures are to be redeemed on the expiry of a certain period. The interest is paid periodically and the initial investment is returned after the fixed maturity period.
4. Irredeemable debentures: These kind of debentures cannot be redeemable during the life time of the business concern.
5. Convertible debentures: Convertible debentures are the debentures whose holders have the option to get them converted wholly or partly into shares. These debentures are usually converted into equity shares. Conversion of the debentures may be:
i) Non-convertible debentures
ii) Fully convertible debentures
iii) Partly convertible debentures
ii) Fully convertible debentures
iii) Partly convertible debentures
6. Other types: Debentures can also be classified into the following types. Some of the common types of the debentures are as follows:
- Collateral Debenture
- Guaranteed Debenture
- First Debenture
- Zero Coupon Bond
- Zero Interest Bond/Debenture
Features of Debentures
1. Maturity period: Debentures consist of long-term fixed maturity period. Normally, debentures consist of 10–20 years maturity period and are repayable with the principle investment at the end of the maturity period.
2. Residual claims in income: Debenture holders are eligible to get fixed rate of interest at every end of the accounting period. Debenture holders have priority of claim in income of the company over equity and preference shareholders.
3. Residual claims on asset: Debenture holders have priority of claims on Assets of the company over equity and preference shareholders. The Debenture holders may have either specific change on the Assets or floating change of the assets of the company. Specific change of Debenture holders are treated as secured creditors and floating change of Debenture holders are treated as unsecured creditors.
4. No voting rights: Debenture holders are considered as creditors of the company. Hence they have no voting rights. Debenture holders cannot have the control over the performance of the business concern.
5. Fixed rate of interest: Debentures yield fixed rate of interest till the maturity period. Hence the business will not affect the yield of the debenture.
Advantages of Debenture
Debenture is one of the major parts of the long-term sources of finance which of consists the following important advantages:
1. Long-term sources: Debenture is one of the long-term sources of finance to the company. Normally the maturity period is longer than the other sources of finance.
2. Fixed rate of interest: Fixed rate of interest is payable to debenture holders, hence it is most suitable of the companies earn higher profit. Generally, the rate of interest is lower than the other sources of long-term finance.
3. Trade on equity: A company can trade on equity by mixing debentures in its capital structure and thereby increase its earning per share. When the company apply the trade on equity concept, cost of capital will reduce and value of the company will increase.
4. Income tax deduction: Interest payable to debentures can be deducted from the total profit of the company. So it helps to reduce the tax burden of the company.
5. Protection: Various provisions of the debenture trust deed and the guidelines issued by the SEB1 protect the interest of debenture holders.
Disadvantages of Debenture
Debenture finance consists of the following major disadvantages:
1. Fixed rate of interest: Debenture consists of fixed rate of interest payable to securities. Even though the company is unable to earn profit, they have to pay the fixed rate of interest to debenture holders, hence, it is not suitable to those company earnings which fluctuate considerably.
2. No voting rights: Debenture holders do not have any voting rights. Hence, they cannot have the control over the management of the company.
3. Creditors of the company: Debenture holders are merely creditors and not the owners of the company. They do not have any claim in the surplus profits of the company.
4. High risk: Every additional issue of debentures becomes more risky and costly on account of higher expectation of debenture holders. This enhanced financial risk increases the cost of equity capital and the cost of raising finance through debentures which is also high because of high stamp duty.
5. Restrictions of further issues: The company cannot raise further finance through debentures as the debentures are under the part of security of the assets already mortgaged to debenture holders.
INTERNAL FINANCE
A company can mobilize finance through external and internal sources. A new company may not raise internal sources of finance and they can raise finance only external sources such as shares, debentures and loans but an existing company can raise both internal and external sources of finance for their financial requirements. Internal finance is also one of the important sources of finance and it consists of cost of capital while compared to other sources of finance.
Internal source of finance may be broadly classified into two categories:
A. Depreciation Funds
B. Retained earnings
Depreciation Funds
Depreciation funds are the major part of internal sources of finance, which is used to meet the working capital requirements of the business concern. Depreciation means decrease in the value of asset due to wear and tear, lapse of time, obsolescence, exhaustion and accident.
Generally depreciation is changed against fixed assets of the company at fixed rate for every year. The purpose of depreciation is replacement of the assets after the expired period. It is one kind of provision of fund, which is needed to reduce the tax burden and overall profitability of the company.
Retained Earnings
Retained earnings are another method of internal sources of finance. Actually is not a method of raising finance, but it is called as accumulation of profits by a company for its expansion and diversification activities.
Retained earnings are called under different names such as; self finance, inter finance, and plugging back of profits. According to the Companies Act 1956 certain percentage, as prescribed by the central government (not exceeding 10%) of the net profits after tax of a financial year have to be compulsorily transferred to reserve by a company before declaring dividends for the year.
Under the retained earnings sources of finance, a part of the total profits is transferred to various reserves such as general reserve, replacement fund, reserve for repairs and renewals, reserve funds and secrete reserves, etc.
Advantages of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings consist of the following important advantages:
1. Useful for expansion and diversification: Retained earnings are most useful to expansion and diversification of the business activities.
2. Economical sources of finance: Retained earnings are one of the least costly sources of finance since it does not involve any flotation cost as in the case of raising of funds by issuing different types of securities.
3. No fixed obligation: If the companies use equity finance they have to pay dividend and if the companies use debt finance, they have to pay interest. But if the company uses retained earnings as sources of finance, they need not pay any fixed obligation regarding the payment of dividend or interest.
4. Flexible sources: Retained earnings allow the financial structure to remain completely flexible. The company need not raise loans for further requirements, if it has retained earnings.
5. Increase the share value: When the company uses the retained earnings as the sources of finance for their financial requirements, the cost of capital is very cheaper than the other sources of finance; Hence the value of the share will increase.
6. Avoid excessive tax: Retained earnings provide opportunities for evasion of excessive tax in a company when it has small number of shareholders.
7. Increase earning capacity: Retained earnings consist of least cost of capital and also it is most suitable to those companies which go for diversification and expansion.
Disadvantages of Retained Earnings
Retained earnings also have certain disadvantages:
1. Misuses: The management by manipulating the value of the shares in the stock market can misuse the retained earnings.
2. Leads to monopolies: Excessive use of retained earnings leads to monopolistic attitude of the company.
3. Over capitalization: Retained earnings lead to over capitalization, because if the company uses more and more retained earnings, it leads to insufficient source of finance.
4. Tax evasion: Retained earnings lead to tax evasion. Since, the company reduces tax burden through the retained earnings.
5. Dissatisfaction: If the company uses retained earnings as sources of finance, the shareholder can’t get more dividends. So, the shareholder does not like to use the retained earnings as source of finance in all situations.
LOAN FINANCING
Loan financing is the important mode of finance raised by the company. Loan finance may be divided into two types:
(a) Long-Term Sources
(b) Short-Term Sources
(b) Short-Term Sources
Loan finance can be raised through the following important institutions.
Financial Institutions
With the effect of the industrial revaluation, the government established nation wide and state wise financial industries to provide long-term financial assistance to industrial concerns in the country.
Financial institutions play a key role in the field of industrial development and they are meeting the financial requirements of the business concern.
Commercial Banks
Commercial Banks normally provide short-term finance which is repayable within a year.
The major finance of commercial banks is as follows:
The major finance of commercial banks is as follows:
Short-term advance:
Commercial banks provide advance to their customers with or without securities. It is one of the most common and widely used short-term sources of finance, which are needed to meet the working capital requirement of the company. It is a cheap source of finance, which is in the form of pledge, mortgage, hypothecation and bills discounted and re-discounted.
Short-term Loans
Commercial banks also provide loans to the business concern to meet the short-term financial requirements. When a bank makes an advance in lump sum against some security it is termed as loan. Loan may be in the following form:
(a) Cash credit: A cash credit is an arrangement by which a bank allows his customer to borrow money up to certain limit against the security of the commodity.
(b) Overdraft: Overdraft is an arrangement with a bank by which a current account holder is allowed to withdraw more than the balance to his credit up to a certain limit without any securities.
Development Banks
Development banks were established mainly for the purpose of promotion and development the industrial sector in the country. Presently, large number of development banks are functioning with multidimensional activities. Development banks are also called as financial institutions or statutory financial institutions or statutory non-banking institutions.
Development banks provide two important types of finance:
(a) Direct Finance
(b) Indirect Finance/Refinance
(a) Direct Finance
(b) Indirect Finance/Refinance
Presently the commercial banks are providing all kinds of financial services including development-banking services. And also nowadays development banks and specialist financial institutions are providing all kinds of financial services including commercial banking services. Diversified and global financial services are unavoidable to the present day economics. Hence, we can classify the financial institutions only by the structure and set up and not by the services provided by them.
long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond,
long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond, long term sources of finance, short term sources of finance, sources of finance pdf, sources of finance notes, sources of finance pdf notes, Sources of finance, sources of financing, long term, short term, based on the period, long term sources of financing, short term sources of financing, equity share, preference share, debenture, long term loans, fixed deposits, equity, debt, debenture, security financing,equity share, preference share, preferred share, convertibles, convertible bond,

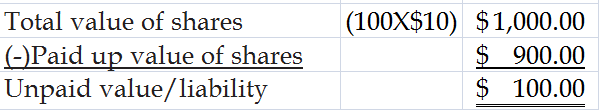


This article is very informative. we create and offer flexible solutions and platforms; lending, funding , ranging from 1 million to 1 billion USD/EUR and above, for any kind of financial need including Start Up Loans with Bad Credit.
ReplyDeletePost a Comment